Mar . 11, 2024 14:13 Back to list
Principle of Metal Mesh
This chapter will discuss what metal mesh is, how it is made, and the design considerations.
What is Metal Mesh?
The phrase "wire mesh" describes two- or three-dimensional structures constructed of two or more metallic wires connected by various techniques. In a wide range of settings, wire mesh products are frequently used for carrying, displaying, fencing, and armoring. As a result, wire mesh is a necessary component of both industry and daily life.
The materials used to create metal mesh sheets include stainless steel, galvanized steel, plain carbon steel, aluminum, copper, bronze, brass, and other specialty metals. Wires of different thicknesses are intertwined, woven, or joined to form parallel rows and intersecting columns that are proportionately equal in size.
The process of creating wire mesh (sometimes referred to as wire fabric, wire cloth, or hardware mesh) entails weaving wire on commercial looms while leaving square or rectangular gaps between the wires. An electric welder is used to join parallel longitudinal wires where they intersect to create welded wire mesh or cloth.
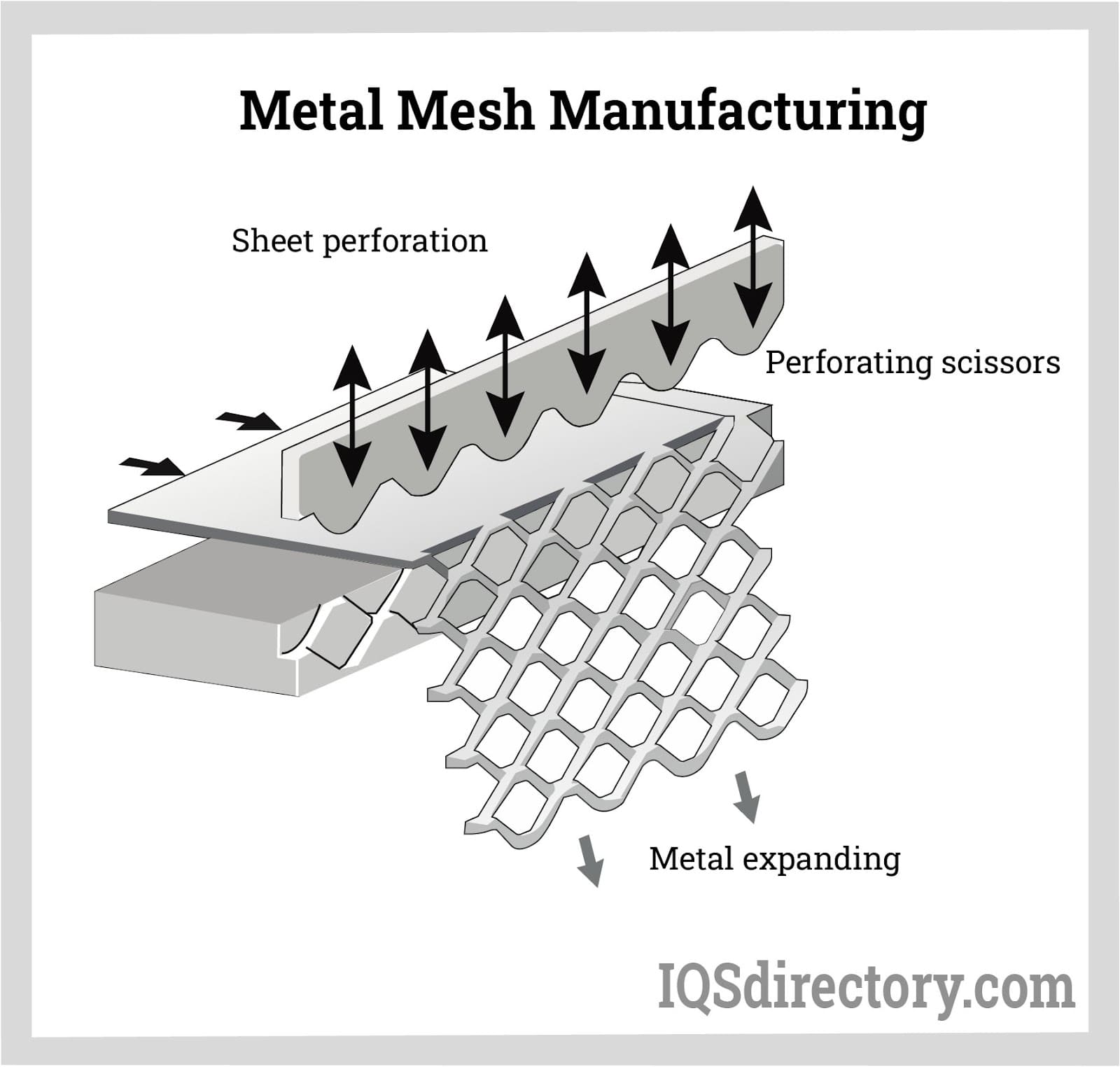
How Metal Mesh is Made
Iron is used to make steel, which has unique and desirable properties. In particular, stainless steel is entirely rust-resistant and extremely durable, making it the ideal choice for a variety of functions in the economy. Steel wires are more useful for creating wire mesh and other products due to their excellent ductile (the ability to be formed into wires) quality combined with their tensile strength and flexibility.
Wire mesh is one of the earliest and most straightforward things made from steel. Steel wire mesh has been used for millennia in one form or another. The world's social economies, which are constantly expanding, have discovered new applications, such as fencing and barricading, safety covers for operating machines, cages, grills, sifters, and shelves.
Iron welded wire mesh is used as concrete reinforcement, which serves another significant purpose. Steel wire maker firms cater to the secondary level ancillaries that utilize these wires to create the mesh through welding or weaving.
Design Considerations for Metal Mesh
- Important characteristics of the mesh, including spacing, opening size, and mesh count, are often determined by the application. Wire cloth is determined by mesh size in some applications and opening size in others.
- The difference between woven and welded construction has the biggest effect on the toughness and durability of metal cloth, with welded wire cloth having the best qualities.
- The weaving affects the strength and durability of different types of woven wire fabric.
- The working environment (temperature, humidity, wet vs. dry, flames, marine salt spray) determines the choice of metal or metal alloy.
- The material is also informed by the media that is processed (wet slurries, dry non-corrosive powders, acids, corrosive chemicals).
- One of the most important characteristics of wire cloth is the diameter of round wire, the width of flat wire, or the breadth of ribbon. Even though several distinct wire gauge systems are in use, some wire cloth manufacturers may define wire size in terms of "wire gauge" size. To avoid confusion, the wire diameter should be calculated using a numerical inch or micron value.
- The number of wires over a unit length, typically a linear inch, measures the mesh size, also known as the wire count or mesh count. The mesh count is calculated from wire center to wire center. The size of very big aperture wire mesh fabric is determined by the space between the two adjacent wires; examples are 1-inch mesh, 2-inch mesh, 58-inch mesh, etc.
Considerations when Choosing Metal Mesh (or Wire Cloth)
The considerations include:
-
Temperature
Understanding temperature limits is crucial when using a fireproof wire mesh in high-temperature applications. Given that any malleable metal or alloy can be used to create woven wire mesh, you should select the best one for a particular procedure. Here are some of the highest working temperatures: stainless steel grade 304 (1500 °F or 815.5 °C); Inconel (1800 °F or 982 °C); nickel (2700 °F or 1482 °C); and tungsten (5000 °F or 2760 °C).
-
Corrosive Effects
Although most wire cloths are prone to corrosion, some materials, including titanium and alloys like Hastelloy, Inconel, and Nichrome, can tolerate more corrosive conditions.
-
Viscosity
Viscosity is crucial in wastewater treatment, oil handling, and other petrochemical filtering. Filters can handle thinner, less dense fluids more quickly. Consider what kind and size of wire mesh are required to process very viscous materials to get the best outcomes. Viscosity frequently has a direct relationship with temperature.
-
Particulate Matter Size
Particle size is an obvious factor to consider when selecting the ideal wire mesh. The mesh count, aperture size, and wire diameter can all be determined using the size of any retained particles. It is important to purchase test sieves to achieve the requirements for retained particulate matter sizes.
-
Pressure Drop Requirements
When materials pass through a filter, the pressure decreases and impurities are eliminated. The filter media you select for your filter significantly impacts the pressure drop rate. The filter will eventually need to be replaced when the pressure decrease reaches a certain level. Effective wire mesh solutions that match your pressure drop criteria decrease costs and contamination hazards.
-
Flow Rates
Viscosity, pressure drop, and flow rate are closely connected. You should consider the percentage of open area when choosing the appropriate mesh product for procedures that specify a required flow rate.
-
Contaminant Types
Certain pollutants will influence the material to be utilized, the wire diameter, the density of the wire mesh, the tolerance, the opening size, and the type of weave.
-
Specific Gravity
Depending on the purpose, wire cloth parameters must frequently be adjusted. Wire cloth mesh baskets and sieves are used for numerous manufacturing processes to gauge and test the specific gravity of a filtered material. These items, which are often made of brass or stainless steel, must be ordered in accordance with your particular gravity testing requirements.
share
-
High Flow Water Filter Cartridge – Superior Filtration & Easy Replacement Hi Flow Water Filter Replacement Cartridge & Aqua Flow 50 Filter Cartridges
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Premium Window and Door Mosquito Net – Effective Insect Protection for Your Home
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Premium Stainless Steel Netting Mesh Discount & ODM Stainless Steel Wire Mesh Solutions
NewsJun.24,2025
-
High-Quality Screen Stone for Modern Stone Screen Walls Elegant Facade Solutions
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High Quality Wire Filter – Cheap Stainless Steel Filter Wire Mesh Cloth & Wire Mesh Filter Solutions
NewsJun.10,2025
-
5 Micron Water Filter Cartridge - Premium Sediment Filtration, Universal Fit
NewsJun.10,2025

